Accessing Plugin Settings
All Plugins are able to be configured using a "PluginSettings" class.
This job of this class is to hold a dictionary of settings accessible to the Plugin class and able to be configured by users from within the Unmanic WebUI.
The Settings class should be included in your Plugin's plugin.py file if you wish
to have the option of enabling configuration options for the Plugin's users.
Example
plugin.py
from unmanic.libs.unplugins.settings import PluginSettings
class Settings(PluginSettings):
"""
An object to hold a dictionary of settings accessible to the Plugin
module and able to be configured by users from within the Unmanic WebUI.
This class has a number of methods available to it for accessing these settings:
> get_plugin_directory() - Returns the absolute path to the Plugin's directory.
This is where the Plugin is currently installed.
> get_profile_directory() - Return the absolute path to the Plugin's profile
directory. This is where where Plugin settings are
saved and where all mutable data for the Plugin
should be stored.
> get_form_settings() - Return the current form settings.
(see class attribute below)
> get_setting(<key>) - Fetch a single setting value. Or leave the
key argument empty and return the full dictionary.
> set_setting(<key>, <value>) - Set a singe setting value.
Used by the Unmanic WebUI to save user settings.
Settings are stored on disk in order to be persistent.
"""
"""
settings
A dictionary of settings accessible to the Plugin class and able
to be configured by users from within the Unmanic WebUI.
In the blow settings:
Boolean Option - will become 'checkbox' in WebUI
Custom String Option - will become text 'input' in WebUI
Advanced - Select dropdown - will become text 'input' in WebUI
(overwritten with form_settings below)
Advanced - Text area input - will become text 'input' in WebUI
(overwritten with form_settings below)
"""
settings = {
"Boolean Option ": True,
"Custom String Option": "",
"Advanced - Select dropdown with custom label": "opt2",
"Advanced - Text area input": "default value",
}
"""
form_settings
A dictionary of form settings used by Unmanic's WebUI to configure
the plugin's settings form.
This dictionary overwrites the defaults applied above and provides more advanced form
configuration for the Plugin user.
Advanced - Select dropdown - will instead become 'select' input in WebUI
Advanced - Text area input - will instead become 'textarea' input in WebUI
"""
form_settings = {
"Advanced - Select dropdown with custom label": {
"input_type": "select",
"select_options": [
{
"value": 'opt1',
"label": 'option 1',
},
{
"value": 'opt2',
"label": 'option 2',
},
{
"value": 'opt3',
"label": 'option 3',
},
],
"label": "Dropdown selection",
},
"Advanced - Text area input": {
"input_type": "textarea",
"label": "Multi-line text area input",
},
}
Available methods
The PluginSettings class has a couple of methods available to it for accessing these settings.
Do not access the Settings class attributes directly. Use the provided methods.
Not using the provided methods will lead to always receiving the default values and not the user configured options.
classmethod get_plugin_directory()
Returns the absolute path to the Plugin's directory. This is where the Plugin is currently installed.
Example:
settings = Settings()
plugin_directory = settings.get_plugin_directory()
db_file = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(plugin_directory, '..', '..', 'config', 'unmanic.db'))
classmethod get_profile_directory()
Return the absolute path to the Plugin's profile directory. This is where where Plugin settings are saved and where all mutable data for the Plugin should be stored.
Example:
settings = Settings()
profile_directory = settings.get_profile_directory()
db_file = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(profile_directory, 'history.db'))
classmethod get_form_settings()
Return the current form settings.
Example:
settings = Settings()
form_settings = settings.get_form_settings()
if form_settings.get('option', {}).get('input_type') == 'textarea':
return True
classmethod get_setting( [key] )
Parameters:
- key (str) – the configuration option key.
Fetches a configuration value from the Settings object. If no key is provided, this method will return a full dictionary of all configured options.
If no library_id is provided to the Settings object, then it will return the global settings. If no config has been saved for the given library_id, this method will fallback to returning the global settings. See example below.
Example:
settings = Settings(library_id=data.get('library_id'))
# Fetch a single value
enable_feature = settings.get_setting('Enable Feature')
# Fetch all options as a dictionary
all_options = settings.get_setting()
classmethod set_setting( key, value )
Parameters:
- key (str) – the configuration option key.
- value – the configuration option value.
The set_setting method is used by the Unmanic WebUI to save
user settings. However you are able to access this method from
your Plugin's functions also.
Settings are stored on disk in order to be persistent across restarts.
If no library_id is provided to the Settings object, then it will be stored in the global settings file. If no config has been saved for the given library_id, this method will create that library's config file. See example below.
Example:
settings = Settings(library_id=data.get('library_id'))
enable_feature = settings.set_setting('Enable Feature', False)
Adding settings to your Plugin
To add settings to your Plugin, simply add a settings dictionary to your Settings class.
There are two basic settings options. Boolean (True/False) and String.
If you enter a default value that is a Boolean, then Unmanic will treat it as such and will
present this option to the user as a <input type="checkbox"> in the Unmanic web UI.
If you enter a default value that is a String, then Unmanic will present this option to the
user as a <input type="text"> in the Unmanic web UI.
Example:
If you are to create a settings class with the following values.
class Settings(PluginSettings):
settings = {
"Boolean Option ": True,
"Custom String Option": "",
}
Then it will be displayed in the browser as:
Advanced form input in WebUI
You can use a basic text and checkbox input form for your Plugin as shown above. In most cases, this should be enough. However, sometimes you may wish to include more advanced form input options to configure your Plugin.
You can overwrite the default form elements with the form_settings class variable.
This class variable can be used to:
- Dynamically show/hide settings
- Mark sub-settings
- Overwrite the input labels
- Create select drop-down inputs
- Create textarea inputs
- Create directory browser inputs
- Create slider inputs
Dynamically show/hide settings
(since v0.1.0)
If you want your Plugin's settings options to change based on the input of other options such as a checkbox,
you can do this by adding an __init__(self) method to your Settings class.
Inside this method, modify the form_settings object according what you need.
Example:
class Settings(PluginSettings):
settings = {
'Limit to specified extensions': False,
"Comma separated list of file extensions to process.": 'ts',
}
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(Settings, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.form_settings = {
"Comma separated list of file extensions to process.": self.__set_allowed_extensions_form_settings(),
}
def __set_allowed_extensions_form_settings(self):
values = {}
if not self.get_setting('Limit to specified extensions'):
values["display"] = 'hidden'
return values
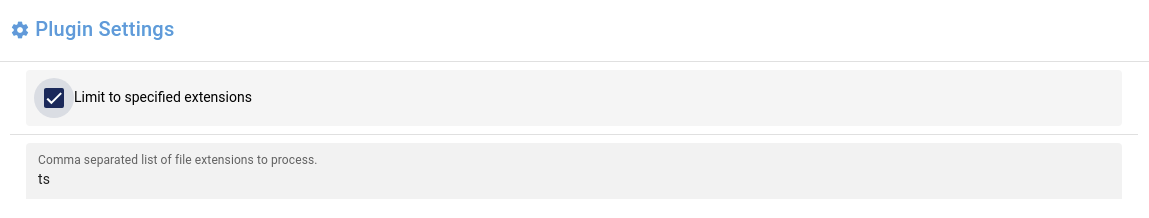
Sub-settings
(since v0.3.0)
If you want a setting to appear visually grouped under another option (for example, a dependent option that only makes sense when a checkbox is enabled), you can mark it as a sub-setting.
Add sub_setting: True to that setting's form configuration to indent it and draw a left border in the WebUI.
Example:
class Settings(PluginSettings):
settings = {
"Enable feature": False,
"Feature level": "medium",
}
form_settings = {
"Enable feature": {
"label": "Enable feature",
},
"Feature level": {
"label": "Feature level",
"input_type": "select",
"sub_setting": True,
"select_options": [
{
"value": "low",
"label": "Low",
},
{
"value": "medium",
"label": "Medium",
},
{
"value": "high",
"label": "High",
},
],
},
}
Overwriting labels
You may wish to have a long, descriptive label for your input field.
Adding a label entry to your form_settings dictionary will overwrite this value in the WebUI
Example:
class Settings(PluginSettings):
settings = {
"my_checkbox": False,
}
form_settings = {
"my_checkbox": {
"label": "Would you like to have this checkbox selected?",
},
}
Select drop-downs
You can use form input select elements if you configure an input_type as "select" entry to your form_settings dictionary.
When you set the input_type as "select", you must also add a list of select_options.
Each select_options should consist of a dictionary containing a value and a label.
Example:
class Settings(PluginSettings):
settings = {
"NVENC Encoder Quality Preset": "medium",
}
form_settings = {
"NVENC Encoder Quality Preset": {
"input_type": "select",
"select_options": [
{
'value': "fast",
'label': "Fast",
},
{
'value': "medium",
'label': "Medium",
},
{
'value': "slow",
'label': "Slow",
},
{
'value': "lossless",
'label': "Lossless (slowest)",
},
],
},
}
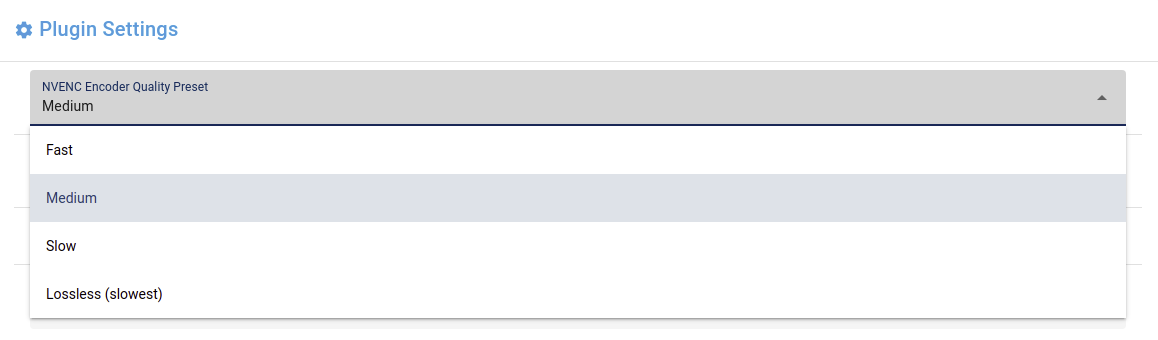
Textarea
You may wish to allow multi-line input for your string variables.
By default, Unmanic's WebUI will treat a string input as a "text" input type. This will generate a <input type="text"> element.
You can override this in Unmanic's WebUI by setting the input_type as "textarea" in your form_settings dictionary.
Example:
class Settings(PluginSettings):
settings = {
"Patterns": "",
}
form_settings = {
"Patterns": {
"input_type": "textarea",
},
}
Select directory
(since v0.0.8)
If you intend to use a text input for specifying a path to a directory, you could use Unmanic's directory select browser popup rather than require the path to be entered manually.
This can be done by setting an input_type as "browse_directory" entry to your form_settings dictionary.
Example:
class Settings(PluginSettings):
settings = {
"Destination directory": "/library/complete",
}
form_settings = {
"Destination directory": {
"input_type": "browse_directory",
},
}
Slider
(since v0.1.0)
If your Plugin config option is to accept an integer and you have a set max/min value, you may wish to use the slider.
This can be done by setting an input_type as "slider" entry to your form_settings dictionary.
Example:
class Settings(PluginSettings):
settings = {
"bitrate": 2000,
}
form_settings = {
"bitrate": {
"label": "Bitrate",
"input_type": "slider",
"slider_options": {
"min": 1000,
"max": 10000,
"step": 100,
"suffix": "K"
},
},
}